Technical article
2025-12-18
In the separation and mass transfer processes for the fields of chemical engineering, environmental protection, energy, etc., the selection of packings determines the efficiency and operating costs of the equipment directly. As a classic and continuously optimized tower packing, metal pall rings continue to play an indispensable and critical role in global industrial applications due to their excellent comprehensive performance.
1、Core Definition and Working Principle: Why is it "Pall Ring"?
The metal pall ring is a revolutionary improvement based on the Raschig ring. It is made by stamping high-quality metal sheets such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum alloy, etc. Its structural feature is that two rows of window holes with inner curved tongue pieces are opened on the ring wall.
This seemingly minor change has brought about a leap in performance.
* Efficient gas-liquid distribution: These windows effectively guide the liquid inside the tower to the inner space of the ring and disperse it to the inner and outer surfaces of the ring wall, greatly improving the uniformity of gas-liquid two-phase distribution.
* Reduce pressure drop and wall flow effect: Compared with traditional packing, the pall ring breaks the "wall effect" of the gas flow path, making the gas flow path more tortuous and free, significantly reducing the system pressure drop, and effectively reducing the "wall flow" phenomenon of liquid flowing down the tower wall.
* Increasing the utilization rate of specific surface area: Gas and liquid phases can form effective liquid films on both the inner and outer surfaces of the ring and the window tongue, resulting in a higher utilization rate of specific surface area and a significant improvement in mass transfer efficiency.
What is the working principle of the pall ring?
Firstly, we need to start with the metal Raschig ring, which is the most traditional metal ring. The liquid tends to flow downwards along the tower wall ("wall flow effect"), and the gas is prone to take a short central path, resulting in a sharp decrease in effective contact area. And with a metal pall ring, the double-layer rectangular windows on the ring wall are like "smart deflectors" designed for fluids. Gas and liquid are forced to enter the internal space of the ring through these windows. This process breaks down and disperses the concentrated large flow, fundamentally disrupting the conditions for the formation of wall flow and channel flow. Liquid forms a uniform liquid film on the surface of metal. Through multiple shunting and internal mixing through the window, the liquid film is continuously "thinned, torn, and rebuilt". This' surface renewal 'effect is crucial as it continuously exposes fresh mass transfer interfaces, keeping the driving force of mass transfer (absorption, desorption, distillation) at a high level, thereby significantly improving mass transfer efficiency.
It's like turning Rasi into a "straight pipeline", where the fluid is easily stratified and passes through quickly; The metal pall ring is a "carefully designed miniature labyrinth reactor" that forces fluids to turn, collide, and mix within it, maximizing contact opportunities and time.
Correct installation of metal pall rings
*Preparation before loading:
1. Cleaning inside the tower: Thoroughly remove welding slag, rust, oil stains, and other debris inside the tower.
2. Check the distributor: Confirm that the initial liquid distributor is level, unobstructed, and secure.
3. Packing inspection: Check the material, specifications, and quantity of the packing, and remove any deformed rings or debris generated during transportation.
Standardized assembly filling steps:
Method A: Dry filling (For small towers or maintenance)
1. Laying the bottom layer: evenly lay a layer of large particle packings or ceramic balls as the bottom layer on the supporting grid plate to protect the grid plate and improve the initial distribution.
2. Manual dispersion filling: The operator enters the tower (ensure safe ventilation!), manually scoops out the filler from the bag, and slowly disperses and spills it. It is strictly prohibited to dump the entire bag!
3. Layered filling and leveling: For each filling of about 500mm in height, use a flat plate or specialized tool to gently scrape and level the filling layer from the tower to the outside, ensuring that the filling layer is absolutely horizontal and checking for any "bridging" or "hollowing" phenomena.
4. Repeat layer by layer: Repeat steps 2-3 until the designed filling layer height is reached. For ultra-high packing layers, it is necessary to set up packing pressure rings or redistributors according to the design.
Method B: Wet filling (Especially for large towers)
1) Inject a certain height of clean liquid (usually water) into the tower.
2) Slowly and evenly pour the packing material into the tower from above the liquid level. Water buffers the impact force of the filler, effectively preventing deformation and dust generation, and can naturally achieve a tighter and more uniform accumulation.
3) During and after the filling process, it is also necessary to drain the liquid and conduct flatness and level checks.
2、Main application areas
The excellent performance of metal pall rings has made them widely used in the following industrial fields:
1). Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
* Distillation tower: Used for the separation and purification of various organic chemicals, solvents, and intermediates.
* Absorption tower: Used to recover valuable components or remove harmful substances from gas streams, such as using wash oil to absorb benzene from coal gas.
* Desorption tower/stripping tower: Used to remove gases dissolved in liquids, such as removing carbon dioxide and oxygen from water.
2). Environmental engineering
* Waste gas treatment (VOCs treatment): Used in scrubbing and adsorption towers to remove acidic gases (such as SO₂, HCl) and organic volatile compounds from industrial waste gas.
* Wastewater treatment: Used in the blow off tower to remove volatile pollutants such as ammonia nitrogen from wastewater.
3). Energy and Metallurgy
* Gas drying and purification: used as a carrier for dehydration and purification in air separation units and natural gas drying towers.
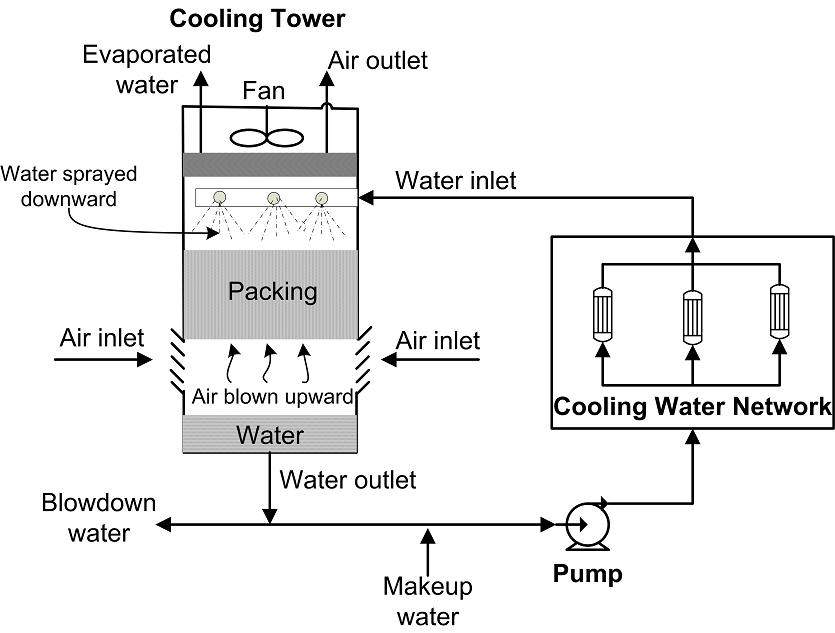
* Cooling tower: It is also used in some high-efficiency cooling towers that require high efficiency and compact structure.
| Name | Pall Ring | Raschig Ring | Intalox Saddle |
| Mass Transfer Efficiency | High | Low | Higher |
| Pressure Drop | Low | High | Midium |
| High Flux | High | Low | Higher |
| Applicable scenarios | Adsorption, distillation, washing tower | Mass trasfer processes with low requests | High gas and high load scenarios |