Technical article
2025-05-26
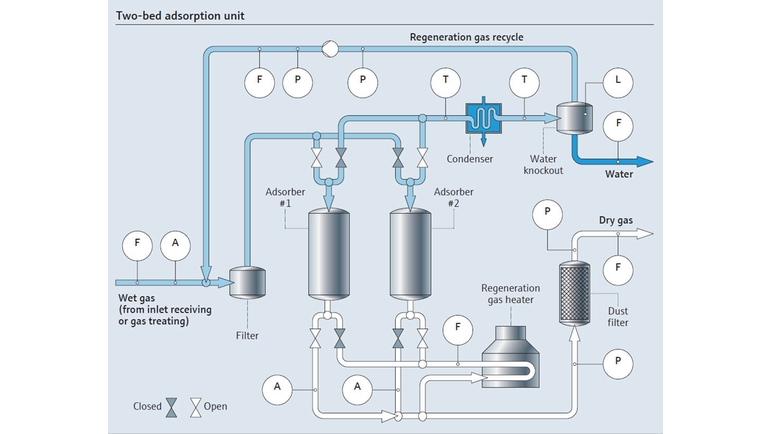
Molecular sieve dehydration method is a relatively efficient dehydration method, which utilizes the special structure and adsorption properties of molecular sieves to adsorb natural gas moisture onto them under certain conditions. This method can achieve continuous operation and automatic control, with good dehydration effect, and can recover and regenerate adsorbents.
One of our customers, who comes from Asia, they need to put our molecular sieve 4A and ceramic balls into a drying tower. Natural gas will pass through this tower, and our molecular sieve 4A desiccant will remove water vapor from the airflow, making the natural gas flowing out from the other side dry. At the same time, our inert ceramic balls will be placed at the bottom and top of the drying tower to protect the molecular sieve from particle damage. This process is very important in the oil and gas industry, as moisture can affect the quality and transportation efficiency of natural gas.
The following is the specific operation process:
Use adsorbents to remove water from natural gas, thereby achieving dehydration. Adsorbents are generally porous materials such as molecular sieves, which have a large surface area and strong adsorption capacity. When natural gas passes through the adsorber, the adsorbent adsorbs water and can also remove other impurities from the natural gas. Next, the adsorbent needs to go through a regeneration process to release the adsorbed water and prepare for another dehydration operation.
Lowering the temperature of natural gas and condensing the water vapor inside into liquid water can achieve the purpose of dehydration. Condensation dehydration is one of the common dehydration methods. Natural gas enters the condenser, and as soon as the temperature drops, water vapor condenses into liquid water. Next, by using a separator to separate natural gas from liquid water, dry natural gas can be obtained.
Contact natural gas with selective absorbents so that water can be absorbed into the absorbents, thereby achieving dehydration. This method may be used in certain specific situations, where natural gas comes into contact with molecular sieve adsorbents and water enters the absorbent, completing the dehydration of natural gas.