Technical article
2025-04-05
Many people confuse carbon molecular sieve and activated carbon easily. Because both carbon molecular sieve and activated carbon are porous carbon materials. But there are essential differences in their design goals, structural characteristics, and industrial applications. This article will analyze it from 4 parts:
Firstly, regarding the application of two adsorbents: Carbon molecular sieve is specially designed for gas molecule screening, achieving gas separation through precisely controlled uniform micropores (0.3-0.5nm). For example, in nitrogen production equipment, the molecular size difference between oxygen (O2 ) and nitrogen (N2 ) (0.346nm vs 0.364nm) is utilized to preferentially adsorb O2 with a faster diffusion rate, thereby enriching high-purity nitrogen gas (>99.9%). Activated carbon is known for its broad-spectrum adsorption, and with its multi-level pore structure (coexistence of micropores, mesopores, and macropores) and surface functional groups, it can efficiently capture large molecule pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pigments, and heavy metals.
Different structures: Carbon molecular sieves form micropores with extremely narrow pore size distribution (deviation<0.02nm) through high-temperature processing, with pore volume concentrated in 0.4-0.6cm3 /g, and surface chemical inertness to avoid non target adsorption; Activated carbon relies on physical/chemical activation to generate a complex pore network with a specific surface area of up to 3000m2 /g. The surface is rich in active groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, making it easy to chemically modify and enhance specific adsorption capabilities.
Significant differences in application conditions:
* Carbon molecular sieves are mainly used in the field of gas separation, such as biogas purification and medical oxygen production. Their high temperature resistance (≤ 300 ℃) supports high-frequency pressure swing adsorption (PSA) cycles.
* Activated carbon is widely used in environmental protection (COD removal from wastewater, air purification) and industrial purification (food decolorization, gold extraction), but it is sensitive to regeneration conditions (high temperature easily destroys functional groups) and has better economic efficiency.
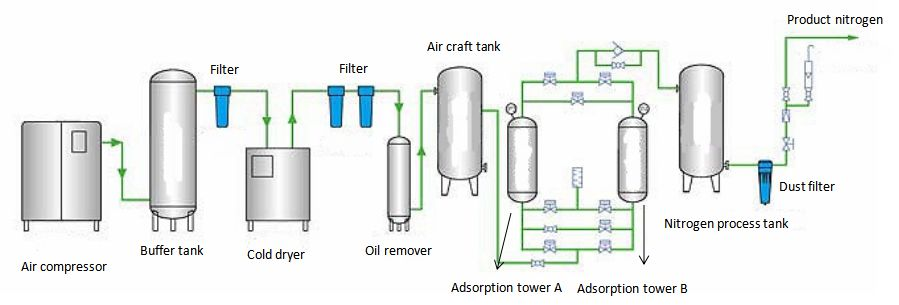
However, the two adsorbents also have common application, such as being used to produce high-purity N2 gas. In the complete set of PSA Nitrogen equipment, activated carbon will be used in the air filter device to remove oil stains in the air, so that the purified air is the gas without impurities such as water vapor and oil, thereby obtaining pure N2 gas.